
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates (POC)
For our peptide oligonucleotide conjugates (POC), biomers.net offers a comfortable conjugation service.
In most cases a direct synthesis of peptide oligonucleotide conjugates is not possible, since the conventional protecting group strategies of oligonucleotide and peptide synthesis are not or only hardly compatible. According to this, oligonucleotide and peptide are first synthesized separately and then linked via reactive linkers, e.g. azide-alkyne (Click Chemistry) or thiol-maleimide. The resulting peptide oligonucleotide conjugate is HPLC purified and characterised by mass spectrometry.
Our service includes the following specific services:
- consultation and etablishing of the individual coupling strategies (thiol-maleimide, alkyne-azide, azide-DBCO) and the
- orientation of oligonucleotide and peptide
- separate synthesis, purification and characterisation of oligonucleotide and peptide
- chemical conjugation of the individual components through reactive linkers
- purification of the conjugate via special HPLC gradients
- characterisation and verification of the conjugate with mass spectrometry and analytical HPLC and CE
The reactive linkers in the oligonucleotide can be at 3´- or 5´-end, so that an oligonucleotide can be attached to a peptide in both orientations. The azide linker is preferably attached to the N-terminus of the peptide, whereas the thiol linker, e.g. via a cysteine, can be found internally or terminally.
We prefer the copper-free linkage via an azide and a DBCO for coupling. Here, the azide can be present either in the form of an azido-hexanoic acid at the N-terminus or a 2-amino-5-azido-n-pentanoic acid (Orn (N3)) at the C-terminus of the peptide. The DBCO may be at the 5´-or 3´-end of the oligo.
| Azide-DBCO coupling between an oligo and a peptide (peptide with terminal azide) |
|---|
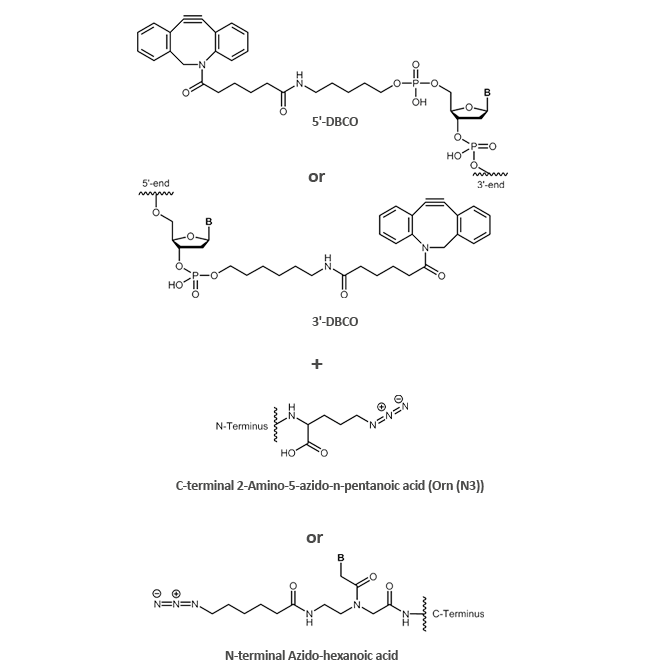 |
| Peptide-oligo conjugate |
|---|
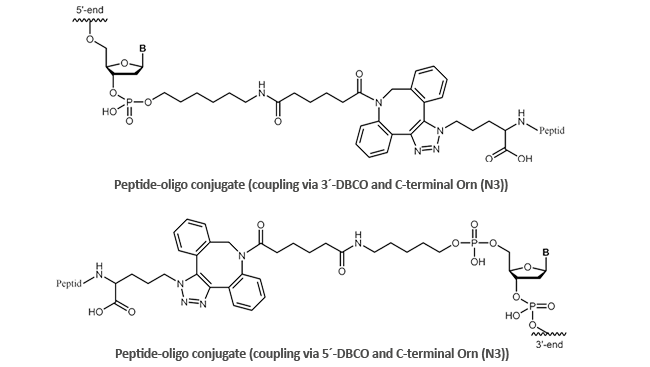 |
Synthetic routes to create oligonucelotide peptide conjugates:
| Azide-alkyne compound between oligo and peptide (peptide with terminal azide) |
|---|
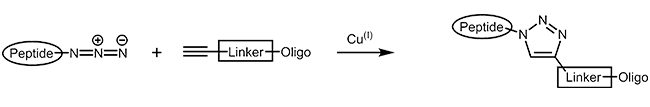 |
| Thiol-maleimide compound to connect the oligo and the peptide (peptide with terminal thiol group) |
|---|
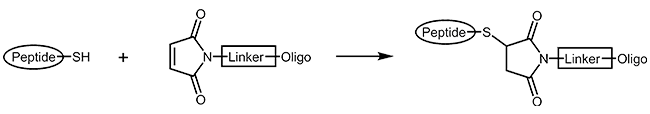 |
Various applications...
In peptide oligonucleotide conjugates, peptides are covalently coupled to the oligonucleotide. In recent years these constructs have become increasingly important for multiple purposes and could be expanded by several interesting alternatives:
- improvement of membrane permeability and transport mechanism of antisense oligonucleotides by coupling of cell-penetrating peptides (CPP)
- covalent linkage of several proteins to the oligonucleotide via sortase reaction (e.g. triglycine)
- affinity tags
- Flag tag (DYKDDDDK) for antibody detection and protein isolation with particular high purity
- His tag (HHHHHH) for purification and isolation of proteins by immobilised metal affinity chromatography
- c-myc tag (EQKLISEEDL, epitop tag) for cellular localisation and purification of the desired proteins
If you need oligonucleotide peptide conjugates with further modifications (e.g. fluorescent dyes) to oligonucleotide or peptide, please contact our customer support team at any time.
We look forward to assist you in realising your personal project.
Tel +49 731 70 396 0 ǀ info@biomers.net

