
Spacer
Spacer
Spacer
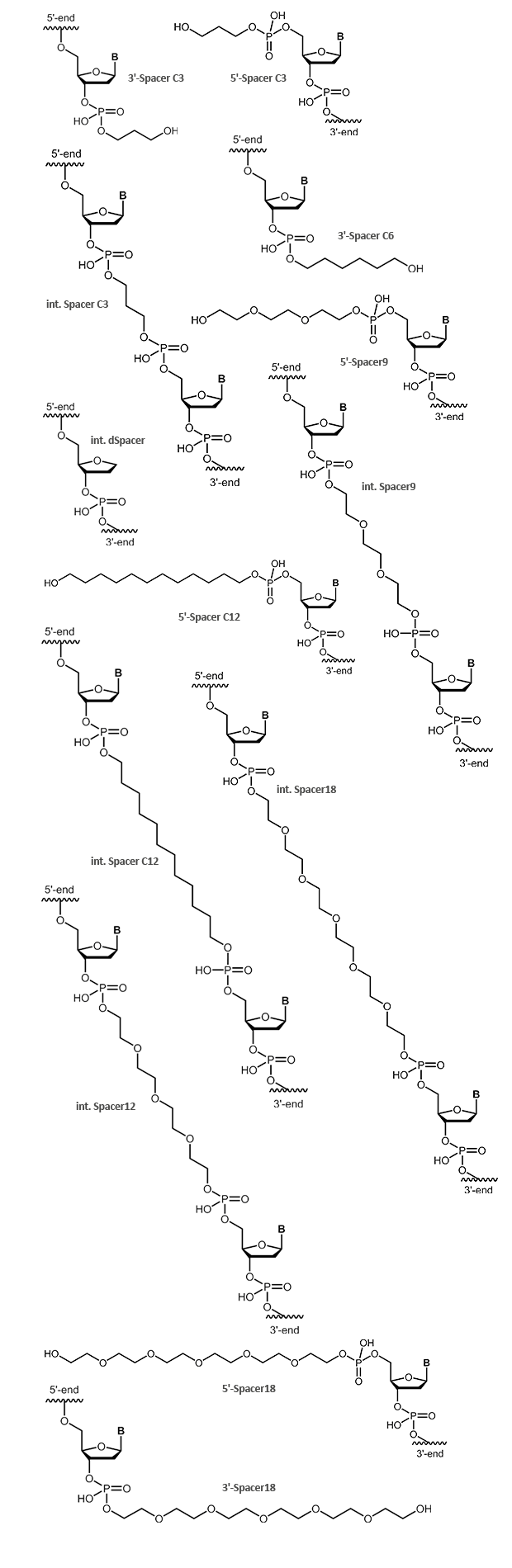
A wide variety of spacers can be incorporated into oligonucleotides, both at the 3´- and 5´-ends, or internally in the nucleotide chain. The ethylene glycol-based spacers (Spacer18 = hexaethylene glycol, HEG, Spacer12 = tetraethylene glycol and Spacer9 = triethylene glycol) are somewhat more hydrophilic than the pure alkyl chains (Spacer C3, Spacer C6 and Spacer C12).
The addition of a Spacer C3 (3 hydrocarbons) to the 3´-end of an oligonucleotide can prevent e.g. its elongation during a PCR without influencing its annealing properties in any meaningful way. Such a modification is therefore well suited for hybridisation probes used in a PCR reaction.
The dSpacer, also referred to as the abasic site, tetrahydrofuran (THF) or apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site, is a non-nucleobase deoxyribose building block, thus the spacing ratios in the oligonucleotide chain remain largely unchanged.
biomers.net offers different terminal and internal spacers:
- Spacer C3, Spacer C6, Spacer C12
- Spacer9, Spacer12, Spacer18
- dSpacer
| Modification | 5´ | 3´ | internal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spacer C3 | x | x | x |
| Spacer C6 | x | x | x |
| Spacer C12 | x | x | x |
| Spacer9 | x | x | x |
| Spacer12 | x | x | x |
| Spacer18 | x | x | x |
| dSpacer | x | - | x |
 |

