
Copper-chelating azides (Cu chelating azides) represent a further development of the azide component in copper(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (“click chemistry”). Unlike conventional organic azides, chelating azides have an additional ligand function (e.g., triazole), which stabilizes the copper(I) center after binding to the azide. The close coordination of copper to the substrate ensures efficient activation of the azide, accelerating cycloadditive ring formation. Furthermore, this stabilization allows for a reduction in the amount of copper (I) catalyst required by up to an order of magnitude compared to conventional systems. Lower catalyst concentrations minimize heavy metal residues in the end product and simplify further processing. In biological applications (e.g., protein or cell labeling), the chelating group also reduces the concentration of free copper ions, which significantly lowers cytotoxicity.
Literatur:
Bevilacqua, V., King, M., Chaumontet, M., Nothisen, M., Gabillet, S., Buisson, D., Puente, C., Wagner, A. and Taran, F. (2014), Copper-Chelating Azides for Efficient Click Conjugation Reactions in Complex Media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 53: 5872-5876. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201310671
Study on the reactivity of various azides in a copper-catalyzed click-reaction
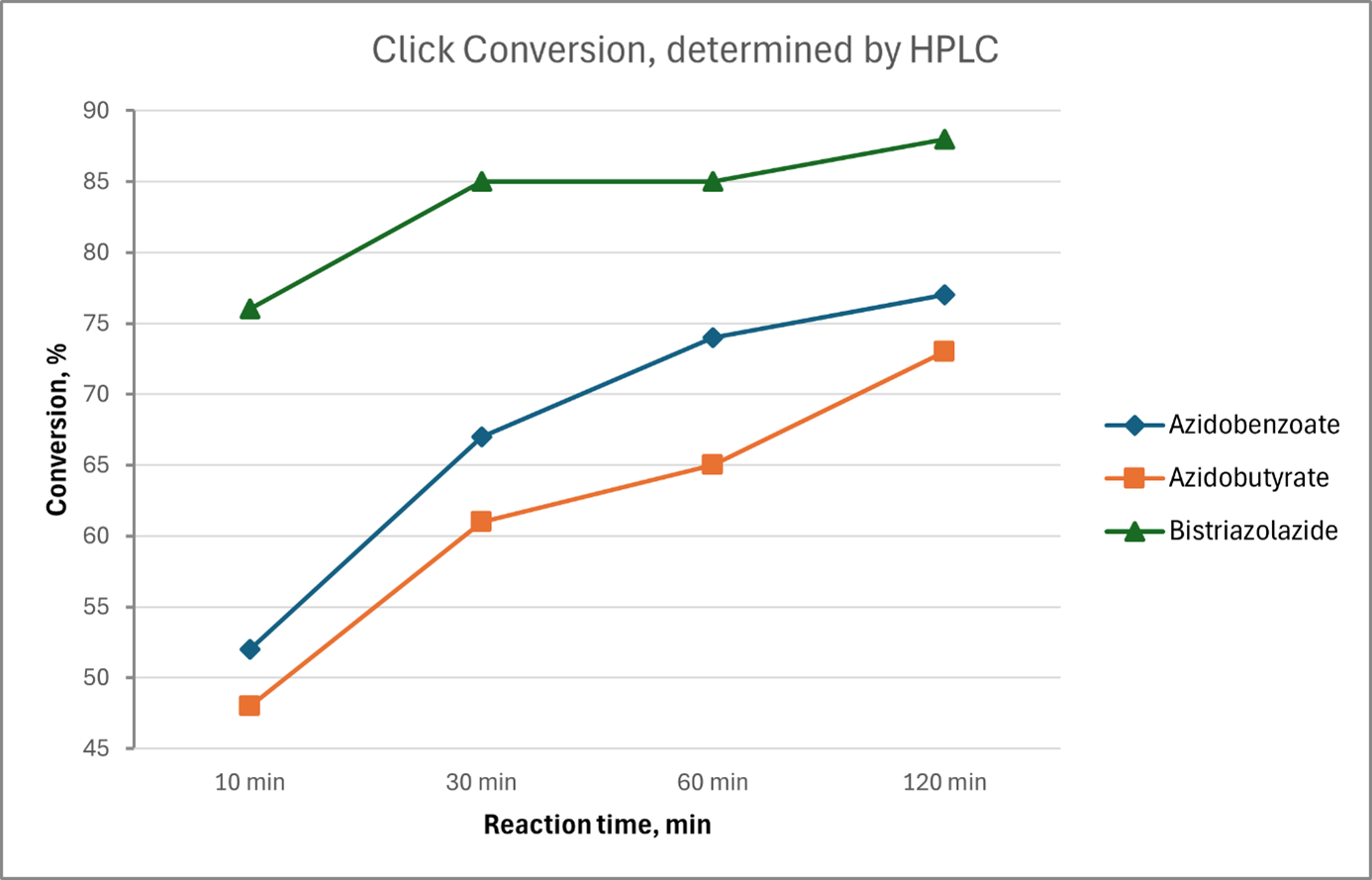
In a model experiment, oligonucleotides (each dT20) were reacted with 5'-azidobutyrate, 5'-azidobenzoate, and 5'-bis-triazolazide in a copper-catalyzed click reaction with one equivalent of BMN-Q480 alkyne in each case. Samples were taken at different times and the progress of the reaction was determined by HPLC analysis. Compared to the other two azides, bis-triazole azide reacts significantly faster and more completely. (If BMN-Q480 alkyne is used in a significant excess (e.g., threefold), all three azides react almost completely after about 10 minutes in our model experiment.)


