
Peptide Nucleic Acids
Properties and application
Peptide Nucleic Acid Oligomers - Molecules with high affinity and sequence selectivity
Peptide nucleic acids or PNA are extremely stable especially in in vivo systems and show notable hybridisation properties.
Peptide nucleic acid is a DNA mimic, which has an uncharged backbone instead of an entire negatively-charged sugar-phosphate backbone. The backbone of peptide nucleic acids consists of repeating N-(2-aminoethyl) glycine units (AEG) linked by peptide bonds.1 The nucleobases A/G/C/T are attached to the backbone via an acetamide linkage.5 Via peptide bonds, PNA can be conjugated easily to peptides or fluorescent dyes, making it interesting for diagnostics and therapeutics.1
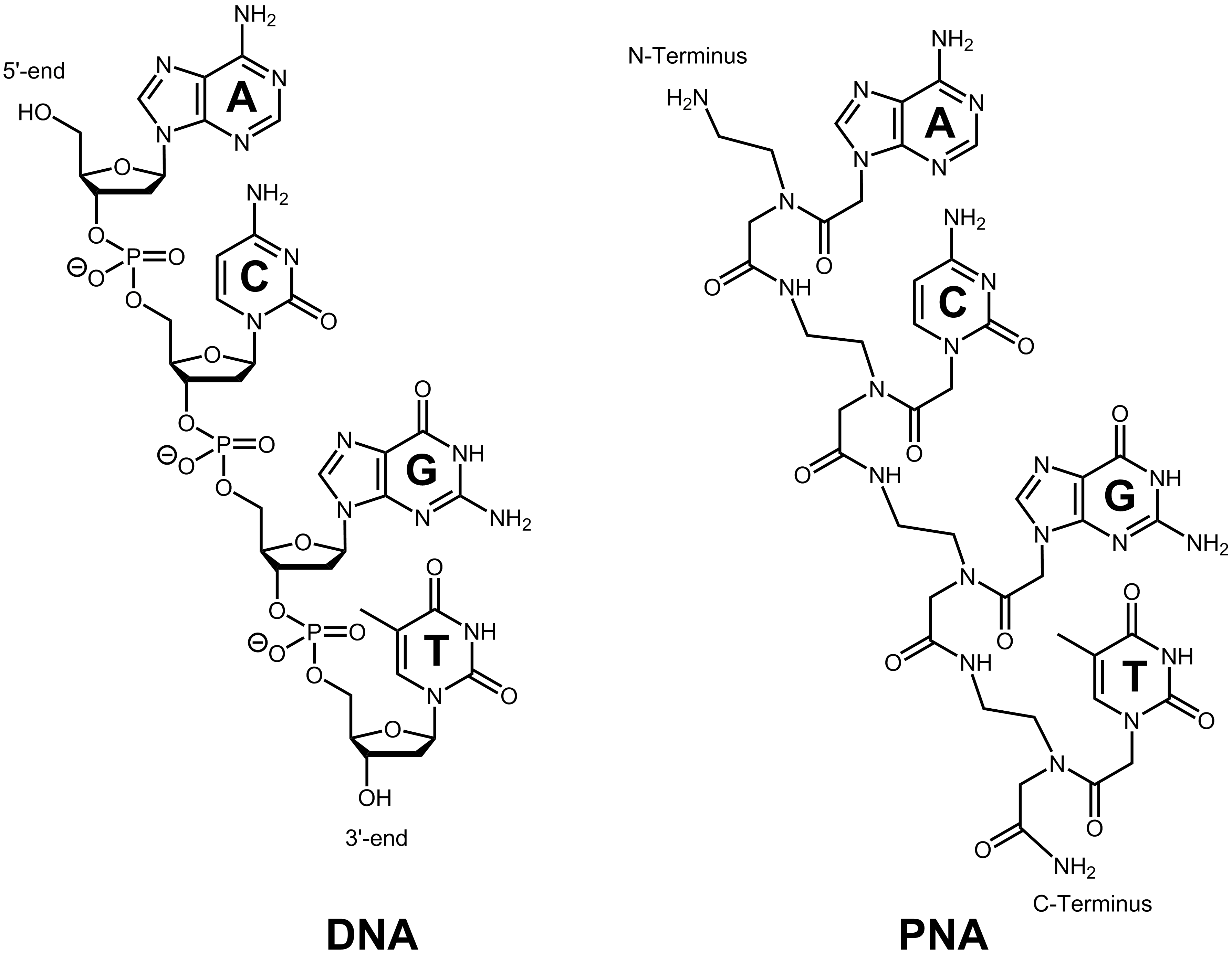 |
Owing to correct intra-molecular spacing and hybridisation between complementary nucleic acids, peptide nucleic acids show a high sequence selectivity and affinity towards DNA or RNA molecules. Via Watson-Crick base pairing, PNA is able to recognize the corresponding complement of DNA or RNA. According to its uncharged backbone, peptide nucleic acids can bind to negatively charged DNA or RNA without any electrostatic repulsion.1 Therefore PNA has a higher binding affinity than native DNA or RNA. The melting temperature is around 1°C higher per base pair compared to DNA/DNA or DNA/RNA molecules. This higher thermal stability and the improved hybridisation properties are independent of the salt concentration present.
Additional positive charged lysine residues in the neutral backbone has shown to enhance the solubility and binding affinity for nucleic acid targets.5
Because of the high binding affinity even the use of short oligomers with only 13-18 bases is efficient.1 PNA also binds very efficiently to complementary sequences of mRNA and thus can modulate its function. It can even break up DNA duplexes and form PNA/DNA triplexes or may form double duplexes without denaturing the DNA duplex.1
Due to its unnatural backbone PNA is resistant to enzymatic degradation (proteases, nucleases). Extreme chemical stability is another feature of PNA.5
According to this, PNA is interesting for many therapeutic and diagnostic applications:
- FISH
- short, very specific and selective probes are possible, extremely stable
- Antisense/Antigene drugs
- high sequence specifity for target in gene sequence
- binding to complementary mRNA and influence of their function
- inhibition of transcription and translation of target genes
- formation of PNA/DNA triplex or double duplex1
- improvement of cellular delivery of PNA by binding of cell penetrating proteins (CPP)5
- blocking of miRNA activity
- SNP detection2
- direct detection of SNP mismatches in DNA fragments
- PCR Clamping and artificial restriction enzymes
- SNP assay (PNA-Clamps for inhibition of polymerase)3,4
- Microarrays and biosensors
- Molecular Beacons2
- Fluorescence detection of specific sequences
Literature:
1. Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) and Its Applications. Wonyong Koh:
Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA) and Its Applications
2. Advantages of Peptide Nucleic Acids as Diagnostic Platforms for Detection of Nucleic Acids in Resource-limited Settings. Zhang N, Appella DH; J Infect Dis. (2010), 201 (Suppl 1): S42-5.
Advantages of Peptide Nucleic Acids
3. Genetic heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines revealed by a rapid and sensitive detection system, the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Nagai Y, Miyazawa H, Huqun, Tanaka T, Udagawa K, Kato M, Fukuyama S, Yokote A, Kobayashi K, Kanazawa M, Hagiwara K.; Cancer Research (2005), 65:7276-82.
4. Peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid polymerase chain reaction clamp-based detection test for gefitinib-refractory T790M epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Nagai Y, Matsuoka M, Huqun, Sutani A, Udagawa K, Zhang J, Hirama T, Murayama Y, Koyama N, Ikebuchi K, Nagata M, Kanazawa M, Nukiwa T, Takenoshita S, Kobayashi K, Hagiwara K; Cancer Sci. (2008), 99(3):595-600.
5. A Review of Peptide Nucleic Acid. Siddiquee S, Rovina K, Azriah A; Advanced Techniques in Biology and Medicine (2015), Volume 3, Issue 2.
Synthesis
Synthesis of peptide nucleic acids
Synthesis of peptide nucleic acids is done similar to solid phase peptide synthesis. The carboxyl group of a PNA building block reacts with the amino group of another building block, resulting in an amide bond.
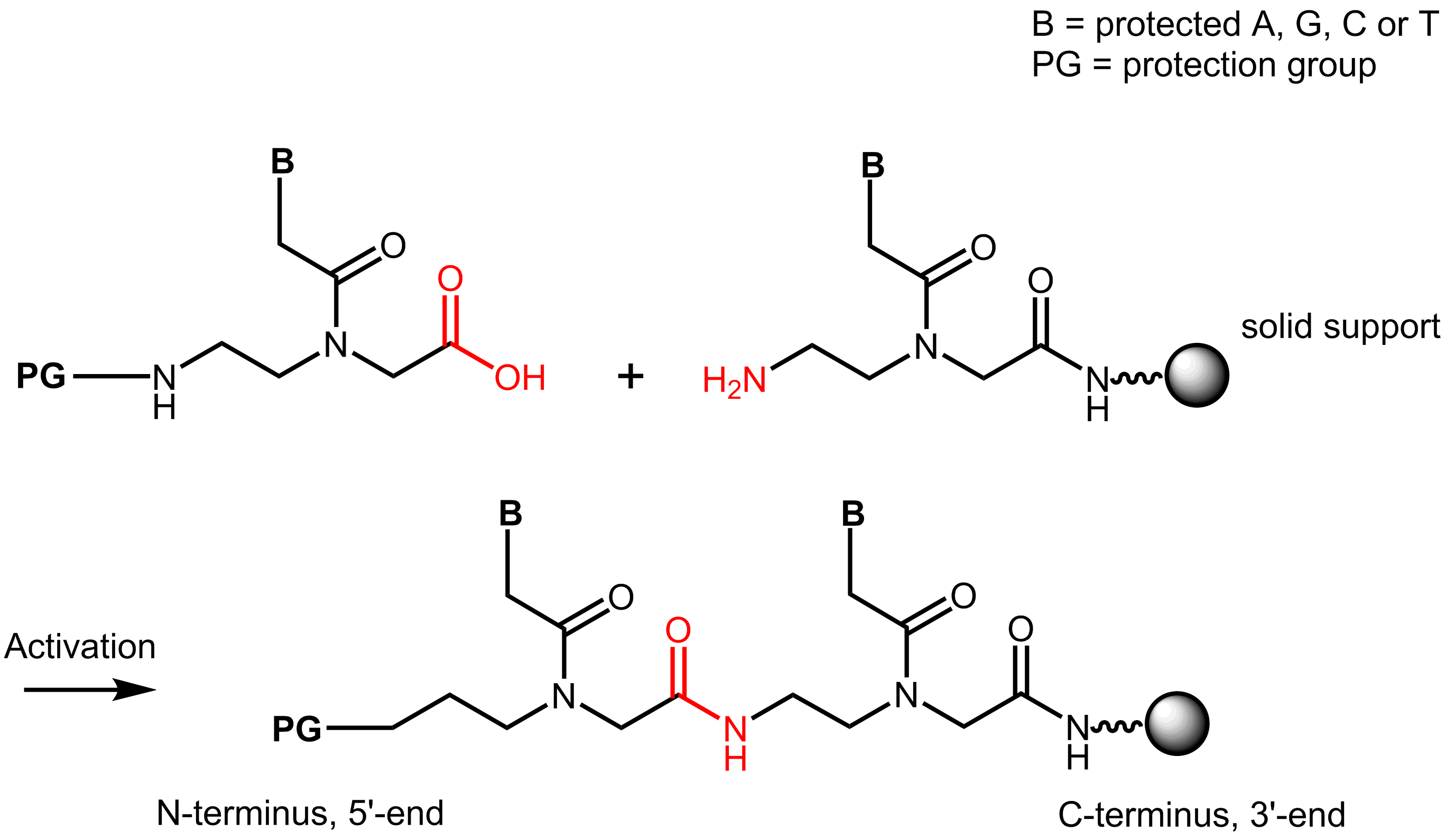
Like in peptide synthesis t-Boc- or Fmoc chemistry can be used. In Fmoc-synthesis the amino group of the N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine building block is protected by an Fmoc group and the amino group of the base is protected by a Bhoc-group.
PNA building blocks:
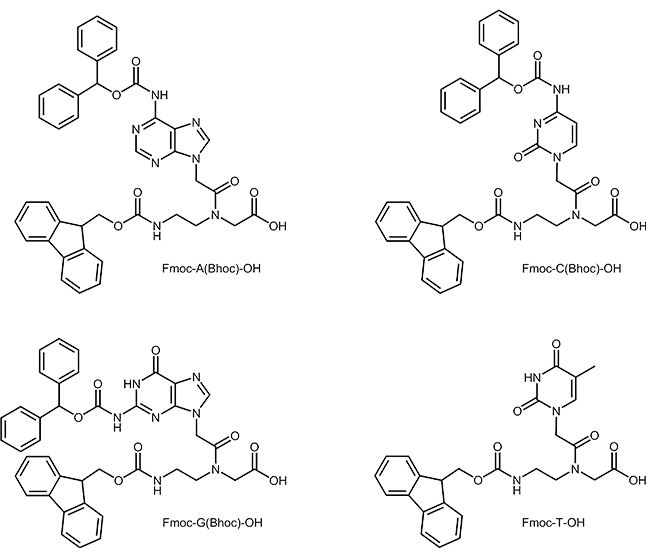
The PNA chain is synthesized on a solid phase, a so called resin. In a first step the C-terminal building block is attached to the resin via its C-terminal carboxyl group. Therefore the synthesis is done from C- to N-terminus.
The synthesis contains a row of synthesis cycles. Each cycle consists of the following steps:
-The amino group of the N-(2-aminoethyl)-glycine is deprotected.
-The carboxyl group of the next building block is activated.
-The next building block is coupled.
-Unreacted amino groups are capped.
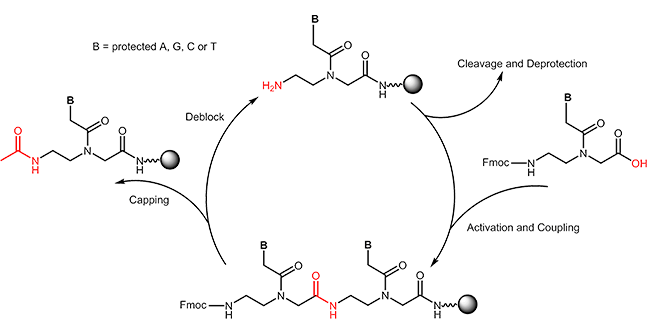
After completion of the PNA chain, it is cleaved from the resin. In this step the Bhoc-protection groups are removed as well.
PNA is purified by RP-HPLC, shorter fragments are removed.1
Literatur:
1. Synthesis of PNA Oligomers by Fmoc-Chemistry. Casale R, Jensen IS, Egholm M; Peptide Nucleic Acids, Protocols and Applications (2004), Horizon Bioscience.
Modifications
N-terminal modifications (corresponds to 5´-terminus)
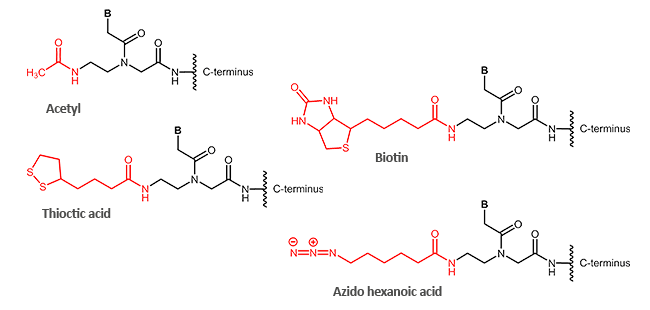
C-terminal modifications (corresponds to 3´-terminus)
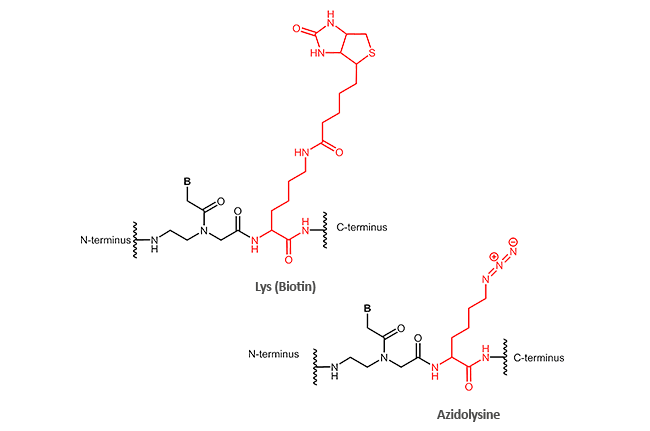
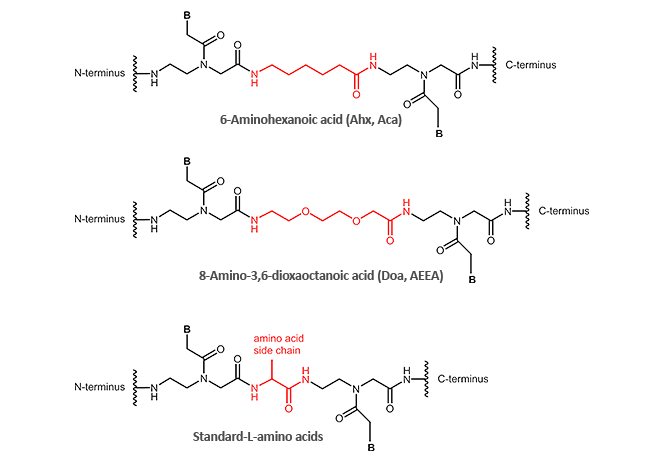
Other modifications (N-terminal, C-terminal or internal)
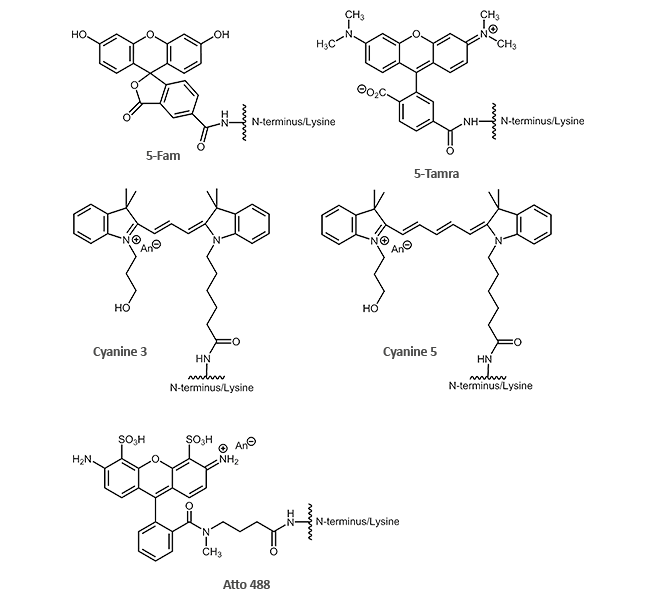
Dyes (N-terminal or via the side chain of Lys):
Ordering
Ordering options
Normally, we offer PNA from 6-25 bases in length and amounts of 30 nmol, 100 nmol and 1 µmol. The purity is approximately 70%, further purification up to 90% is possible and can be also ordered. The identity and purity of each PNA are proved by Maldi mass spectrometry and analytical HPLC respectively.
Because of the resin used, the C-terminus of the PNA is an amide.
It has been shown that with increasing length (from about 5 bases) homopolymeric sequences (in particular poly-T and poly-A) tend to form strong aggregations, which may impair the solubility in aqueous solutions.
biomers.net offers peptide nucleic acid oligomers in cooperation with INTAVIS Peptide Services GmbH.
The synthesis of PNA oligonucleotides takes about 6-8 weeks. Depending on the complexity of the PNA, the synthesis can also take longer.
Ordering:
Ideally, you order directly through our convenient and easy online ordering system. The online ordering ensures the quickest processing of your order and shows the corresponding price even before sending the order.
Alternatively, you can send quote requests or orders with our Excel order sheet to info@biomers.net.
Other modifications are possible on request. Contact us!
For further information, please do not hesitate to contact our customer support team.
We stay at your disposal at any time!
Tel +49 731 70 396 0 I info@biomers.net

